New Research: Curcumin with Turmeric Essential Oil Reverses Aluminum Toxicity
It may be news to your patients, but each day, we ingest or absorb about 10 mg of aluminum. This might not sound like much, but over time it adds up. Once this metal crosses the blood-brain barrier, it increases the risk of developing Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis.
Fortunately, curcumin blended with turmeric oil can help.
A leading-edge study found that a curcumin blended with turmeric essential oil (TEO) crosses the blood brain barrier as well. This means that the botanical’s powerful anti-inflammatory actions can protect delicate brain cells from the toxic effects of aluminum and other metals.
What This Means for Your Patients
What makes this new study so exciting is that blending curcumin and TEO not only allows curcumin to benefit nearly every organ of the body, it helps curcumin pass through the blood-brain barrier to extend these benefits to brain tissue, as well. This is a key difference, because not all curcumin has been proven to do this.
This unique and proven curcumin also stays in the bloodstream longer, so it can protect and preserve brain cells better. In fact, compared with standard curcumin, the blend of curcumin and turmeric essential oil raised free curcumin levels in the brain almost 14 times higher!
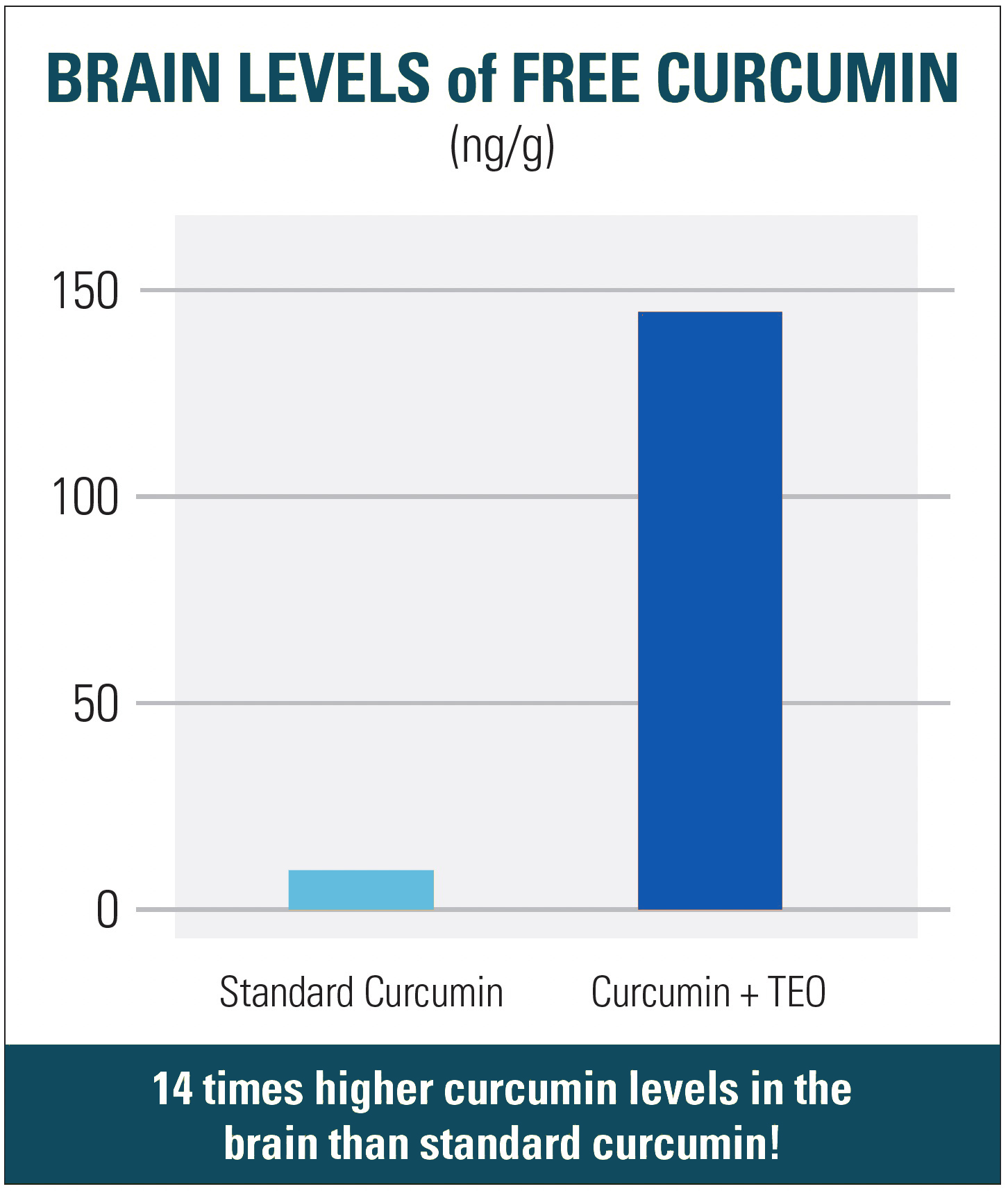
This study went on to look at the effects of curcumin with turmeric essential oil in protecting brain tissue from aluminum toxicity. The researchers found that in an animal model of aluminum toxicity, curcumin with turmeric essential oil reversed the negative effects of aluminum on brain function, boosted levels of glutathione, and improved test results. Additionally, this blend completely protected special brain cells involved in memory.
The bottom line is, this curcumin has amazing potential to prevent numerous neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, depression, and a wide range of other inflammatory, brain, and nerve-related conditions.
And these new findings simply reinforce why curcumin—blended with turmeric essential oil for boosted absorption and better blood retention—is truly the all-in-one-solution to virtually every health challenge your patients may face.
This is great news for any patient with a personal or family history that puts them at increased risk of neurological diseases. That’s because the dosages of this enhanced absorption curcumin—backed by over 90 published studies—are easy to incorporate into any daily regimen.
We recommend: 750 mg of curcumin blended with turmeric essential oil containing 500 mg of curcuminoids twice daily.
The Study Abstract:
Banji D, Banfi OJF, Srinivas K. Neuroprotective effect of turmeric extract in combination with its essential oil and enhanced brain bioavailability in an animal model. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6645720
Purpose. The study evaluated the neuroprotective effect and pharmacokinetic profile of turmeric extract and their metabolites in the blood and brain in an aluminum-induced neurotoxic animal model.
Methods. Swiss albino mice received turmeric extract (TE), TE essential oil combination (TE+EO) at doses of 25 and 50 mg/kg/day orally, vehicle (control), and a positive control group. Neurotoxicity was induced by injecting aluminum chloride (40 mg/kg/day, i.p.), and the effect of the intervention was studied for 45 days. The pharmacokinetic and behavioral biochemical markers of brain function and brain histopathological changes were evaluated.
Results. The AUC 0-t showed a 30.1 and 54.2 times higher free curcumin concentration in plasma with 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg of TE+EO vs. TE, respectively. The concentration of free curcumin in the brain was 11.01 and 13.71-fold higher for 25 mg/kg and 50 mg/kg of TE+EO vs. TE, respectively. Aluminum impairs spatial learning and memory, which was significantly reversed with TE+EO by 28.6% (25 mg/kg) and 39.4% (50 mg/kg). In the elevated plus maze test, 44.8% (25 mg/kg) and 67.1% (50 mg/kg) improvements were observed. A significant reduction in aluminum-induced lipid peroxidation was observed. Also, the levels of glutathione, acetylcholinesterase, and catalase were improved with TE+EO. Damage to the hippocampal pyramidal cells was averted with TE+EO.
Conclusion. The neuroprotective and antioxidant response confirms the benefits of TE+EO against aluminum-induced neurotoxicity. The presence of free curcumin and its metabolites in the brain and plasma establishes its improved bioavailability and tissue distribution. Therefore, the benefits of TE+EO could be harnessed in neurodegenerative diseases.


