ANDROGRAPHIS AND CURCUMIN STOP COLON CANCER
Curcumin and Andrographis Exhibit Anti-Tumor Effects in Colorectal Cancer via Activation of Ferroptosis and Dual Suppression of Glutathione Peroxidase-4 and Ferroptosis Suppressor Protein-1.
Miyazaki K, Xu C, Shimada M, Goel A. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Mar 2;16(3):383.
Background: Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide. The limitations of current chemotherapeutic drugs in CRC include their toxicity, side effects, and exorbitant costs.
Methods: To assess these unmet needs in CRC treatment, several naturally occurring compounds, including curcumin and andrographis, have gained increasing attention due to their multi-targeted functionality and safety vs. conventional drugs.
Results: In the current study, we revealed that a combination of curcumin and andrographis exhibited superior anti-tumor effects by inhibiting cell proliferation, invasion, colony formation, and inducing apoptosis. Genome-wide transcriptomic expression profiling analysis revealed that curcumin and andrographis activated the ferroptosis pathway. Moreover, we confirmed the gene and protein expression of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX-4) and ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP-1), the two major negative regulators of ferroptosis, were downregulated by this combined treatment. With this regimen, we also observed that intracellular accumulation of reactive oxygen species and lipid peroxides were induced in CRC cells. These cell line findings were validated in patient-derived organoids.
Conclusion: In conclusion, our study revealed that combined treatment with curcumin and andrographis exhibited anti-tumorigenic effects in CRC cells through activation of ferroptosis and by dual suppression of GPX-4 and FSP-1, which have significant potential implications for the adjunctive treatment of CRC patients.
Colon cancer is the second deadliest cancer in America. Even with early detection, it can become resistant to conventional chemotherapy drugs, making treatment extremely difficult. This study found that although andrographis and curcumin are strong cancer fighters individually, as a combination they were incredibly effective. This is another example of the enormous potential of botanical medicines to stop cancer and save lives.
What This Means For You:
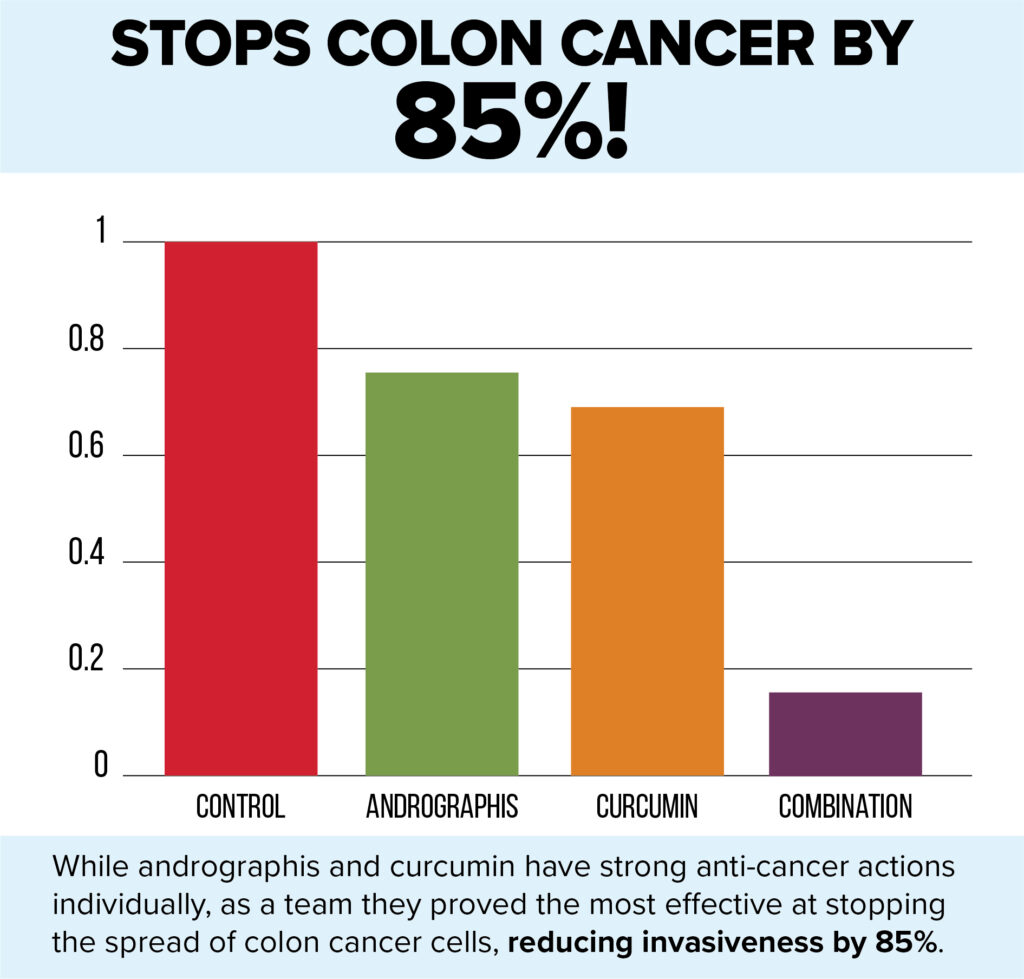
• Andrographis and curcumin combined reduced colon cancer cells by 75%
• Both herbs in combination reduced colon cancer invasiveness (spread) by 85%
• Together, andrographis and curcumin were 10 times stronger in activating the ferroptosis pathway, a natural process that kills cancer cells
Stopping Colon Cancer is Critical!
Colon cancer is the second leading cause of cancer death in the United States. Although regular colon cancer screening tests (such as colonoscopies) have made early detection more common, for 20 percent of colon cancer patients, their cancer will have already spread by the time it is discovered. Unfortunately, cancer cells quickly develop resistance to conventional chemotherapy drugs. This makes it difficult to find treatments that kill cancer, while not killing the patient. So finding other safe and effective options is critical.
Both andrographis and curcumin (a disease-fighting compound from turmeric) have shown strong actions against colon cancer cells in the past, so this study examined andrographis (EP80) and curcumin (BCM-95) individually and in combination, to test and compare their efficacy. The researchers also conducted sophisticated molecular pathway analyses to learn more about how andrographis and curcumin exert their anti-cancer effects.
As expected, curcumin and andrographis individually were very effective at reducing the number of colon cancer cells–each cut the number of cancer cells by up to 60 percent. But when combined, the results were even stronger, reducing them by 75 percent.
Similarly, curcumin and andrographis individually reduced colon cancer invasiveness by 45 to 75 percent. Here again, the combination was best, reducing cancer cell spread by 85 percent.
Combining these botanicals also made them 10 times more effective at activating a cancer-stopping pathway in the body called ferroptosis. Ferroptosis is a process that kills cancer cells by flooding them with iron, creating intensive oxidative damage, and ultimately leading to cancer cell death.
Because of the aggressive nature of colorectal cancer, and the complications of conventional chemotherapy, this research provides great hope for identifying more effective and less toxic treatments that can be used to reduce the burden of cancer.


