IBS, CROHN’S DISEASE, COLITIS, AND OTHER DIGESTIVE DISORDERS
INFOMEDICA’S BOTTOM LINE:
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s Disease, ulcerative colitis, and other digestive disorders can be very difficult to treat conventionally. Prescription medicines can cause side effects that make the cure almost as bad as the disease.
Boswellia has the ability to inhibit 5-LOX and help stop the inflammation-caused symptoms of IBS, Crohn’s, and other concerns. This botanical:
- Stops bloating and pain
- Relieves diarrhea and urgency
- Provides soothing relief and regularity
- Stops bloody diarrhea and intestinal damage
- Equals effectiveness of drugs without side effects
Digestive diseases are common, disruptive, and frustratingly difficult for conventional medicine to treat effectively. In addition to common digestive ailments brought on by viruses, stress, or diet, each day millions of Americans suffer from irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis. These are serious concerns that need to be addressed, but conventional medications often bring a world of unwanted side effects, too.
Fortunately, there is a botanical ingredient that stops the painful inflammation that marks these conditions, and it does so without side effects. This natural medicine? Boswellia.
Boswellia—Nature’s Gift to Us
Boswellia serrata is naturally found in the dry hilly areas of India, and has been used in Ayurvedic medicine for thousands of years. In fact, much of our current knowledge of the healing properties of boswellia originates in India. Research and further clinical studies have substantiated the traditional use of this botanical to treat various conditions, including asthma, arthritis, intestinal/bowel disease, ulcers, bronchitis and many skin disorders.
The strong interest in boswellic acids from the plant comes from clinical research into their anti-inflammatory actions. One of the reasons boswellia is so valuable is the way it fights inflammation. Prescription and over-the-counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) fight inflammation by seriously impeding the COX-1 and COX-2 inflammatory cascades, which can cause a whole host of dangerous side effects. These side effects include erosion of the stomach lining, gastrointestinal bleeding and ulcers, and a reduction in kidney function which doubles the risk of heart attack and stroke.
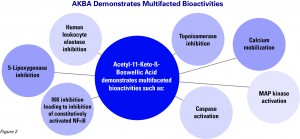
Boswellia works on the 5-LOX cascade, which creates an increase in leukotrienes and results in specific types of inflammation. 5-LOX is the culprit behind chronic gut inflammation, not the COX-1 and 2 cascades. That is why boswellia is extremely effective for irritable/inflammatory bowel, Crohn’s and other intestinal issues, where inflammation drugs fail. Other botanicals may reduce oxidative stress and damage, and in turn, reduce inflammation. They work well, but aren’t as direct as boswellia on the 5-LOX pathway.
Most specifically, boswellic acids are the compounds responsible for the botanical’s effects. The most active of the boswellic acids is known as AKBA (Acetyl-11-keto-B-boswellic acid).
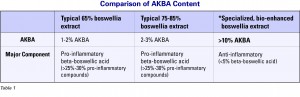
AKBA, a very important boswellic acid that is strongly anti-inflammatory, can have levels as low as one percent in unstandardized boswellia products. Ideally, a boswellia standardized to a minimum of 10 percent AKBA is best. It retains a natural level of the compound without artificially spiking it. Researchers have also found that one of the boswellic acids, beta boswellic acid, is actually PRO-inflammatory—clearly the last thing anyone needs when dealing with inflammatory bowel disease.
The best products are purified and this beta boswellic acid filtered out. Unstandardized products can have as much as 25 percent, so again, the proper standardization is key for the best results.
With digestive disorders, stopping inflammation in a targeted way matters a great deal. For example, microscopic inflammation through the small bowel and colon may be another physical cause—and certainly an effect—of IBS. The already inflamed tissue causes the body to release inflammatory mediators that affect the enteric nerves, and change the way the digestive system reacts to what would otherwise be normal operating procedure. In other words, the inflammation of the gut sends a signal to the brain telling it that something is wrong. The digestive system reacts (or overreacts) by shifting into high gear, in the case of diarrhea, or slowing peristalsis dramatically, in the case of constipation.
As digestive disorders go, IBS is one of the most frustrating for patients and practitioners. Unfortunately, it is also one of the most commonly diagnosed. It’s estimated that 1 in 5 Americans have IBS. Of those individuals, at least 50 percent are referred to a gastroenterologist after reporting symptoms to their primary care doctor. These symptoms range from cramping, bloating and general digestive discomfort to diarrhea and alternating constipation. Many people who suffer from IBS can’t predict when it will occur, so travel plans – and sometimes daily life—can be difficult at best. In the worst cases, individuals need to know at all times where the nearest restroom is located.
Aside from IBS, Crohn’s disease affects over two million Americans between the ages of 15 and 40, it can recur after the age of 50. Crohn’s disease can permeate the intestinal tract and cause fever, pain, bloody diarrhea, and loss of appetite.
Another digestive concern, ulcerative colitis, is an inflammation of the colon that can destroy patches of the mucosal lining of the colon or rectum. Aside from pain, symptoms also include bloody diarrhea and stools that contain mucus or pus.
Plus, these conditions impair the body’s ability to absorb nutrients and deliver them to the bloodstream, which can result in a deficiency of several major nutrients and cause anemia and weight loss. Drugs and surgery have been the standard treatment, particularly for colitis. Unfortunately, these drugs have major side effects, while boswellia has virtually none.
In fact, in a recent study conducted in Germany and Austria, participants with Crohn’s disease were treated with either boswellia or the drug mesalazine (a drug commonly used to treat Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis, and IBS). The results of the study definitely favored boswellia. The authors concluded that boswellia performed as well as the drug, but without the dangerous side effects. In fact, considering safety and efficacy, boswellia showed a much better benefit-to-risk ratio than the drug.
In a clinical study of individuals with colitis, (another condition requiring inhibition of 5-LOX), patients were given boswellia extract or the prescription drug sulfasalazine. The results for boswellia were very positive. Of the 20 patients treated with boswellia, 18 showed an improvement in one or more of the diagnostic parameters, including stool properties and mineral excretion. A follow-up study showed similar results, again positive for boswellia. The authors concluded that boswellia could be an effective treatment because of this – and the lack of side effects.
To stop the inflammation and other symptoms of IBS and other digestive problems, boswellia combined with a high-absorption curcumin extract can help. Curcumin supports the intestines and digestive tract, and is an excellent herbal pain reliever and anti-inflammatory to stop IBS or other digestive flare-ups. In recent studies, the inflammation inhibitory abilities of curcumin suggest that it may help stop micro inflammation in the colon.
The best curcumin extract for this purpose is blended with turmeric essential oil (also a source of ar-turmone) for enhanced absorption and blood retention at meaningful levels compared to standard curcumin extracts.
Patients with Digestive Disorders Can Have a Regular Life
Individuals with IBS, Crohn’s, colitis, or other digestive disorders, can consider lifestyle tips that will help note and reduce symptoms. For instance, keeping a food journal makes it more likely to see patterns in food or behavior that add up to digestive discomfort and stress.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol. Sodas, coffee and tea can make emotions feel “revved up” and begin the spiral of emotional reactions that can lead to IBS symptoms. Alcohol, considered to have a calming influence, can actually cause inflammation in the digestive tract.
- Avoid wheat (and other grains), refined sugar, and dairy products. Any one of these, or a combination of them, can cause physical reactions that make IBS and other digestive disruptions more likely. There is some relationship between people with Celiac disease, who cannot digest gluten, (and have to avoid wheat, rye, barley, and oats) and symptoms of IBS.
- Regular exercise is an effective and healthy way to deal with stress. Even a walk around the block at lunchtime or during a break can make people feel much more grounded and calm. When anxiety seems insurmountable, patients may want to consider discussing it with a professional who can help them work through tough situations more productively.
For Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s Disease, ulcerative colitis, and other digestive disorders, boswellia standardized for AKBA and B-boswellic acid content along with high absorption curcumin or other supportive botanicals is a recommended natural medicine.


